- cross-posted to:
- arstechnica_science@rss.ponder.cat
- cross-posted to:
- arstechnica_science@rss.ponder.cat
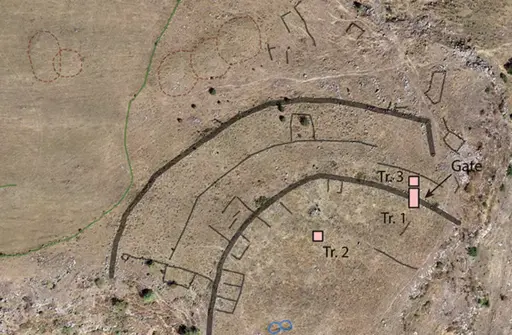
The half-buried Bronze Age ruins of Dmanisis Gora perch on a windswept promontory a few kilometers away from a cave where Homo erectus (or a close relative) lived 1.8 million years ago. Deep, steep-sided gorges run along two sides of the promontory, and sometime between 1500 and 1000 BCE, people stacked boulders into a double layer of high, thick walls to block off the end of the plateau from the plains to the west. Sheltered between the 4-meter high, 2.5-meter wide walls and the 60-meter-deep gorges, people built dugout houses, then later aboveground stone ones, along with stone animal pens and other buildings.
Outside the walls lay a more sprawling, less densely packed settlement, sheltered by another wall to the west. That outer wall was as high and wide as the inner ones, and it stretched a full kilometer from the edge of one gorge to the edge of the other. Between the walls, homes and other buildings formed small compounds with open space between them. Fenced fields, animal pens, and graves dotted the area.